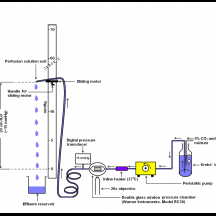
Persons who have glaucoma commonly have increased hydrostatic pressure within the eye. They also have optic nerve damage. Some years ago we devised a way to study the effect of pressure on optic nerve astrocytes. The diagram shows a device that allows us to raise pressure and test how cytoplasmic composition changes. Astrocytes cultured on a glass slide are placed in a sealed pressure chamber (Warner Instruents RC30) and perfused with solution. Pressure is increased by raising the outflow port. By loading the astrocytes with a dye that signals pH we discovered an effect of pressure on sodium-hydrogen exchanger NHE-1.

